Different Types of Multi-Factor Authentication Methods: A Comprehensive Guide
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a security process that requires multiple methods of authentication from the user to gain access to a system, device, or application. This security method is becoming increasingly popular as cyberattacks continue to rise, making it more important than ever to protect sensitive information. MFA is a simple but effective way to add an extra layer of security to your accounts and prevent unauthorized access.
There are several types of multi-factor authentication methods, each with its own unique advantages and disadvantages. The most common types of multi-factor authentication are knowledge-based, possession-based, and biometric-based authentication. Knowledge-based authentication requires the user to provide something they know, such as a password or a PIN. Possession-based authentication requires the user to provide something they have, such as a smart card or a mobile device. Biometric-based authentication requires the user to provide something they are, such as a fingerprint or facial recognition.
Key Takeaways
- Multi-factor authentication is an essential security process that requires multiple methods of authentication from the user to gain access to a system, device, or application.
- The most common types of multi-factor authentication are knowledge-based, possession-based, and biometric-based authentication.
- Each type of multi-factor authentication has its own unique advantages and disadvantages.
Fundamentals of Multi-Factor Authentication
What is Multi-Factor Authentication?
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a security process that requires users to provide two or more forms of identification before being granted access to a system. The purpose of MFA is to add an extra layer of security to user accounts and protect against unauthorized access. The most common forms of identification used in MFA are:
- Something you know (such as a password or PIN)
- Something you have (such as a smart card or token)
- Something you are (such as a fingerprint or facial recognition)
By requiring multiple forms of identification, MFA makes it more difficult for hackers to gain access to sensitive information. Even if a hacker steals a user’s password, they would still need to provide additional forms of identification to gain access to the system.
Benefits of Multi-Factor Authentication
MFA provides several benefits over traditional single-factor authentication methods. Some of these benefits include:
- Increased security: MFA adds an extra layer of security to user accounts, making it more difficult for hackers to gain access to sensitive information.
- Reduced risk of data breaches: With MFA, even if a hacker gains access to a user’s password, they still need to provide additional forms of identification to gain access to the system.
- Compliance: Many industries and organizations are required by law to use MFA to protect sensitive information.
- Improved user experience: While MFA may seem like an inconvenience, it provides a higher level of security and peace of mind for users.
In summary, MFA is a security process that requires users to provide two or more forms of identification before being granted access to a system. By adding an extra layer of security, MFA helps protect against unauthorized access and reduces the risk of data breaches.
Common Multi-Factor Authentication Methods
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a security process that requires users to provide two or more authentication factors to gain access to an application or system. Here are some common multi-factor authentication methods that are widely used:
SMS-Based Verification
SMS-based verification is one of the most common multi-factor authentication methods. It involves sending a one-time password (OTP) to the user’s mobile phone via SMS. The user then enters the OTP into the application or system to complete the authentication process. SMS-based verification is easy to use and cost-effective, but it has some security limitations. For example, SMS messages can be intercepted, and SIM cards can be cloned.
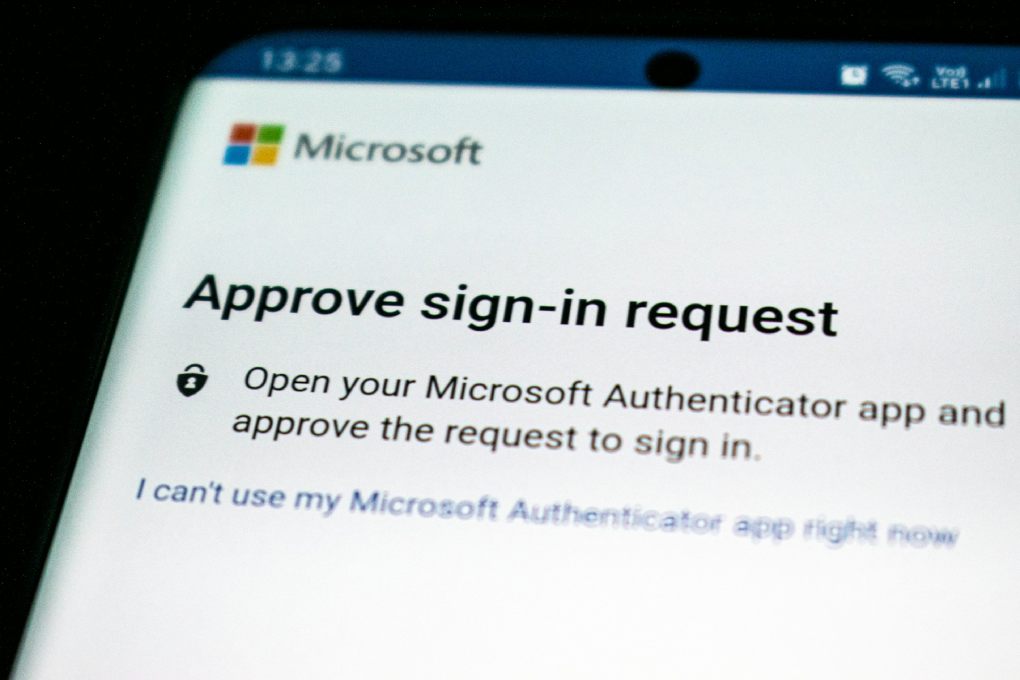
Authenticator Apps
Authenticator apps are another popular multi-factor authentication method. They generate one-time passwords that users can use to authenticate themselves. Authenticator apps are more secure than SMS-based verification because they don’t rely on SMS messages, which can be intercepted. Authenticator apps are also more convenient because users don’t have to wait for an SMS message to arrive. Some popular authenticator apps include Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, and Authy.
Hardware Tokens
Hardware tokens are physical devices that generate one-time passwords. They are more secure than SMS-based verification and authenticator apps because they are not connected to the internet and cannot be hacked remotely. Hardware tokens are also more convenient than authenticator apps because they don’t require a mobile phone. However, hardware tokens can be lost or stolen, and they can be expensive to replace.
Biometric Verification
Biometric verification is a multi-factor authentication method that uses biometric data, such as fingerprints or facial recognition, to authenticate users. Biometric verification is more secure than passwords because biometric data is unique to each individual. Biometric verification is also more convenient because users don’t have to remember passwords. However, biometric data can be stolen or copied, and some users may have privacy concerns about biometric data.
Push Notifications
Push notifications are a multi-factor authentication method that involves sending a notification to a user’s mobile phone. The user then approves or denies the authentication request from the notification. Push notifications are more secure than SMS-based verification because they are encrypted and cannot be intercepted. Push notifications are also more convenient than SMS-based verification because they don’t require the user to enter a one-time password. However, push notifications can be delayed or lost if the user’s mobile phone is not connected to the internet.
Elevate Your Security with Onsite Logic’s Multi-Factor Authentication Solutions
Navigating the various multi-factor authentication methods can be overwhelming, but it’s critical in safeguarding your digital presence. Onsite Logic is your trusted partner in implementing robust MFA strategies tailored to your needs.
Ready to upgrade your cybersecurity?
Connect with Onsite Logic, where we specialize in state-of-the-art cybersecurity solutions. Our expertise in MFA ensures that your data remains protected in an ever-evolving digital landscape. Let’s fortify your security together.
With Onsite Logic, experience cybersecurity that’s as unique as your fingerprint.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common examples of multi-factor authentication in use today?
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is becoming increasingly popular as a way to enhance cybersecurity. Some common examples of MFA in use today include:
- SMS or text message codes
- One-time passwords (OTP)
- Biometric authentication (such as fingerprint or facial recognition)
- Smart cards or tokens
- Push notifications
Which services offer two-factor authentication for enhanced security?
Many popular online services now offer two-factor authentication for enhanced security. Examples include:
- Google (for Google accounts and services)
- Dropbox
- Microsoft (for Microsoft accounts and services)
Who are the leading providers of multi-factor authentication solutions?
There are many providers of MFA solutions, including both established companies and startups. Some of the leading providers include:
- Duo Security
- Okta
- RSA Security
- Microsoft
- Ping Identity
How does multi-factor authentication enhance cybersecurity?
MFA enhances cybersecurity by requiring users to provide more than one form of authentication in order to access a system or service. This makes it much more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access, as they would need to compromise multiple factors (such as a password and a biometric scan) rather than just one.
What is the difference between two-factor and multi-factor authentication?
Two-factor authentication (2FA) requires users to provide two forms of authentication in order to access a system or service, while multi-factor authentication (MFA) requires three or more. MFA is generally considered to be more secure than 2FA, as it provides an additional layer of protection.
Can you explain the various factors involved in four-factor authentication?
Four-factor authentication (4FA) is a type of MFA that requires users to provide four different forms of authentication in order to access a system or service. These factors might include something the user knows (such as a password), something the user has (such as a smart card), something the user is (such as a biometric scan), and somewhere the user is (such as a specific location). 4FA is considered to be one of the most secure forms of authentication available, but it can also be more complex and expensive to implement.